Get Better AI Answers: Your Guide to Chain-of-X Prompting Methods
TL;DR
Chain-of-X prompting methods help AI think step-by-step through your business problems, delivering clearer, more accurate answers whilst reducing errors. These techniques transform vague AI responses into structured, actionable insights you can trust. From simple reasoning chains to advanced verification methods, you'll find the right approach for any business challenge.
Blog Outline
• Who this guide is for & outcomes
• Quick chooser: Pick the right method
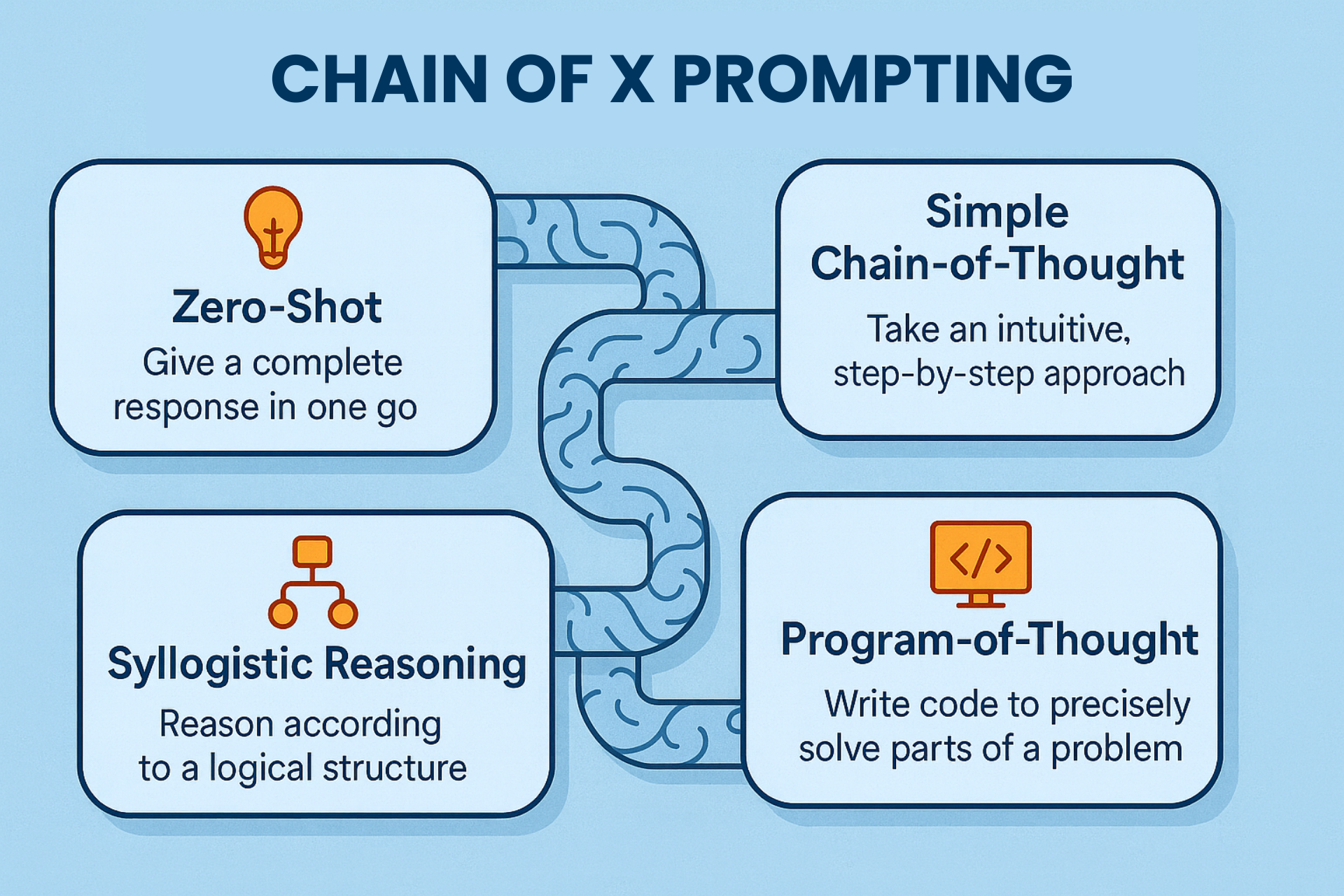
• Chain of Thought (CoT)
• Strategic CoT (SCoT)
• Self-Organised CoT (SOCOT)
Improvement Methods
• Chain-of-Guidance (CoG)
• Understanding-Before-Reasoning (ISP2)
Exploration Methods
• Chain of Draft (CoD)
• Tree of Thoughts (ToT)
Verification Methods
• Chain-of-Verification (CoV)
• Causalised CoT (CauCoT)
Advanced Methods
• Program-of-Thought (PoT)
• Concept-Guided CoT (CGCoT)
• Chain-of-Reasoning (CoR)
Core Methods Explained (Method Cards)
- Chain of Thought (CoT) - Foundation method
- Chain-of-Guidance (CoG) - Question improvement
- Understanding-Before-Reasoning (ISP2) - Information processing
- Strategic CoT (SCoT) - Planning before execution
- Chain of Draft (CoD) - Ultra-concise reasoning
- Tree of Thoughts (ToT) - Multiple path exploration
- Chain-of-Verification (CoV) - Self-checking
- Causalised CoT (CauCoT) - Cause-effect tracking
- Program-of-Thought (PoT) - Code-based reasoning
- Self-Organised CoT (SOCOT) - AI chooses approa
- Chain-of-Reasoning (CoR) - Multi-mode reasoning
- Concept-Guided CoT (CGCoT) - Layered analysis
- Constrained CoT (CCoT) - Length-limited reasoning
- Syllogistic Reasoning (SR-FoT) - Formal logic
Copy-and-paste prompt templates
Nine specific SMB scenarios with ready-to-use prompts:
- Local café: Weekday footfall promotion (CoG)
- Dental clinic: Treatment page rewrite from messy notes (ISP2)
- Fashion e-commerce: Product page conversion mini-audit (SCoT)
- Marketing agency: Monthly PPC summary under token budget (CoD)
- Plumbing services: Winter boiler offer selection (ToT)
- Fitness studio: T&Cs refresh with self-check (CoV)
- Café sales dip: Diagnosis with cause→effect chain (CauCoT)
- Boutique retailer: Simple Q4 revenue projection (PoT)
- B2B SaaS: Onboarding drop-off analysis (SOCOT)
Practical checklist: how to brief AI effectively
Frequently Asked Questions
Appendix: Resources Used
- Research Papers & Studies Referenced
Who this guide is for & outcomes
- Small business owners who want AI to give practical, structured answers instead of generic fluff
- Marketing teams needing AI to analyse campaigns properly, not just surface-level observations
- Service businesses wanting AI to diagnose problems systematically, like a consultant would
- E-commerce managers requiring AI to audit and optimise with clear reasoning
- Agencies needing AI to create client deliverables with transparent logic
- Anyone frustrated by AI giving different answers each time you ask the same question
Quick chooser: Pick the right method
THE BIG THREE - Start here:
- Basic step-by-step thinking? → Chain of Thought (CoT) - AI explains each step
- Need a plan before acting? → Strategic CoT (SCoT) - AI plans strategy, then executes
- Complex problem, unsure approach? → Self-Organised CoT (SOCOT) - AI picks its own method
IMPROVEMENT METHODS:
- Want to guide AI with better questions? → Try Chain-of-Guidance (CoG)
- Analysing before solving? → Use Understanding-Before-Reasoning (ISP2)
EXPLORATION METHODS:
- Need multiple draft versions? → Implement Chain of Draft (CoD)
- Exploring different solutions? → Use Tree of Thoughts (ToT)
VERIFICATION METHODS:
- Want AI to double-check itself? → Try Chain-of-Verification (CoV)
- Tracking cause and effect? → Apply Causalised CoT (CauCoT)
ADVANCED METHODS:
- Mixing code with reasoning? → Use Program-of-Thought (PoT)
- Comparing options systematically? → Use Concept-Guided CoT (CGCoT)
- Complex multi-mode reasoning? → Use Chain-of-Reasoning (CoR)
Core methods explained
Method Card: Chain of Thought (CoT)
What it is:
The foundation of all chain methods. You ask AI to "think step by step" through a problem, showing its working like a maths teacher would. Instead of jumping to conclusions, AI breaks down complex questions into manageable chunks.
When to use:
- Solving multi-part business problems
- Calculating budgets or financial projections
- Troubleshooting operational issues
- Making decisions with multiple factors
When NOT to use:
- Simple yes/no questions
- When you need ultra-quick responses
- Creative brainstorming (too rigid)
Why it helps:
- Significantly reduces errors in complex reasoning tasks
- Makes AI's logic transparent and checkable
- Catches mistakes before they compound
SMB example prompt:
Think step by step about this problem:
My café's weekday footfall dropped 25% last month. Walk-through costs are €8 per customer, average spend is €12. I have €500 for promotions.
Step 1: Calculate current profit per customer
Step 2: Determine break-even for promotions
Step 3: Suggest targeted weekday offers within budget
Show your reasoning at each step.
Method Card: Chain-of-Guidance (CoG)
What it is:
Before answering, AI improves your question through rephrasing and comparison. It transforms vague queries into precise, context-rich questions that generate better answers. Think of it as having an expert interviewer refine your brief.
When to use:
- Starting new marketing campaigns with unclear goals
- Defining project requirements
- Exploring strategic options
- When you're not sure what to ask
Why it helps:
- Substantially improves answer quality through better question formulation
- Uncovers hidden aspects of your challenge
- Saves time by preventing back-and-forth clarification
SMB example prompt:
Improve my question before answering:
Original: "How can I get more weekday customers to my café?"
Step 1: Generate 3 better versions of this question
Step 2: Compare what each version would reveal
Step 3: Create the best final question combining all insights
Step 4: Answer that optimised question with specific tactics
Budget constraint: €500/month
Location: Dublin city centre near offices
Current issue: 25% drop in weekday footfall
Method Card: Understanding-Before-Reasoning (ISP2)
What it is:
AI first digests and structures all information before solving your problem. Like a consultant who spends time understanding your business before making recommendations. The AI extracts key facts, evaluates their reliability, then reasons through the solution.
When to use:
- Processing messy customer feedback or notes
- Analysing complex service offerings
- Reviewing contracts or terms
- Converting rough ideas into structured content
Why it helps:
- 7.1% improvement in solution accuracy (research-proven)
- Better handles incomplete or unclear information
- Reduces misunderstandings of your requirements
SMB example prompt:
First understand, then solve:
STEP 1: Extract key information from these messy notes
STEP 2: Rate reliability of each piece (1-5)
STEP 3: Identify what's missing or unclear
STEP 4: Structure the information clearly
STEP 5: Now write the treatment page
My dental clinic notes: "wisdom teeth extraction info needed, mention sedation options we have LA and IV, recovery 3-7 days usually, cost €300-600 depending, need to mention risks but not scare people, aftercare important - salt rinses etc, when to call us back"
Target: Nervous patients googling "wisdom tooth removal Dublin"
Tone: Reassuring but professional
Method Card: Strategic CoT (SCoT)
What it is:
AI creates a strategic plan before executing. Unlike basic CoT which dives straight into solving, SCoT first maps out the entire approach. Like hiring a consultant who first develops a strategy document, then implements it. The AI identifies resources needed, potential obstacles, then follows through systematically.
When to use:
- Planning marketing campaigns
- Developing service packages
- Optimising conversion funnels
- Restructuring operations
Why it helps:
- Prevents wandering off-track
- Ensures all aspects are considered upfront
- Creates reproducible processes
SMB example prompt:
Strategic planning first, then execution:
PLANNING PHASE:
1. Analyse the problem and constraints
2. Identify available methods/channels
3. Map out step-by-step approach
4. List success metrics
EXECUTION PHASE:
Follow the plan to solve:
Fashion e-commerce product page audit request:
- Product: Women's summer dresses
- Current conversion: 1.2%
- Budget for changes: €2,000
- Timeline: 2 weeks
- Main issue: High add-to-cart but low checkout completion
Provide a strategic audit focusing on quick wins.
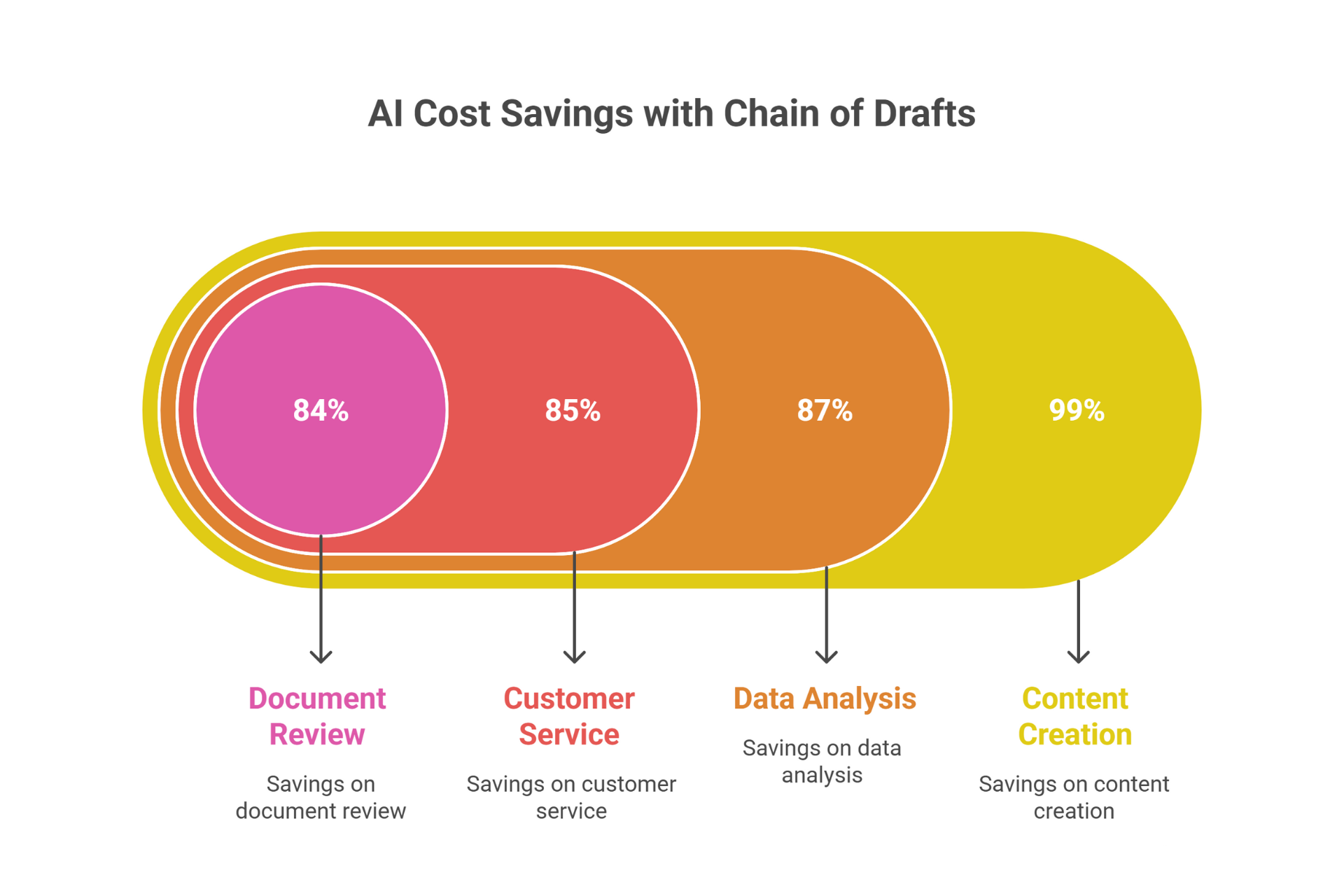
Method Card: Chain of Draft (CoD)
What it is:
AI creates ultra-concise reasoning steps (5 words max per step) before the final answer. Like writing bullet points on a napkin before a presentation. Removes fluff whilst maintaining accuracy.
When to use:
- Quick financial calculations
- Rapid decision-making
- Comparing multiple options
- When AI usage costs matter (charged per word)
Why it helps:
- Uses only 8% of the words (massive cost savings on AI usage)
- Forces clarity and focus • Same accuracy as verbose methods
SMB example prompt:
Draft reasoning (max 5 words per step), then conclude:
Marketing agency PPC summary task:
- Client budget: €5,000/month
- Current CPC: €2.50
- Conversion rate: 2%
- Customer value: €150
- Token limit: Keep draft reasoning minimal
Draft steps:
Clicks possible: 5000/2.50 = 2000
Conversions expected: 2000 × 0.02
Revenue projection: 40 × 150
ROI calculation: 6000 - 5000
Verdict: Profitable, scale carefully
Final summary: [Provide full client summary based on draft logic]
Method Card: Tree of Thoughts (ToT)
What it is:
AI explores multiple solution paths simultaneously, like a chess player thinking several moves ahead. It considers different approaches, evaluates each, and picks the best route rather than committing to the first idea.
When to use:
- Choosing between service packages or offers
- Solving problems with multiple valid solutions
- Strategic decision-making
- When the obvious answer might be wrong
When NOT to use:
- Time-sensitive decisions (takes longer)
- Simple problems with clear solutions
- When you need consistent, reproducible answers
Why it helps:
- Finds optimal solutions, not just acceptable ones
- Avoids getting stuck in poor approaches
- Considers trade-offs explicitly
SMB example prompt:
Explore multiple paths, then choose best:
Plumbing service winter offer selection:
- Budget: €1,000 for promotion
- Goal: Fill quiet January period
- Current services: Boiler repair, bathroom fitting, emergency callouts
- Typical January: 30% below average
Path 1: Boiler servicing discount
- Pros: Timely, high demand
- Cons: Low margin service
- Evaluate: [Reasoning]
Path 2: Bathroom fitting early-bird special
- Pros: High value work
- Cons: Longer lead time
- Evaluate: [Reasoning]
Path 3: Maintenance package deal
- Pros: Recurring revenue
- Cons: Complex to explain
- Evaluate: [Reasoning]
Best path: [Choose with justification]
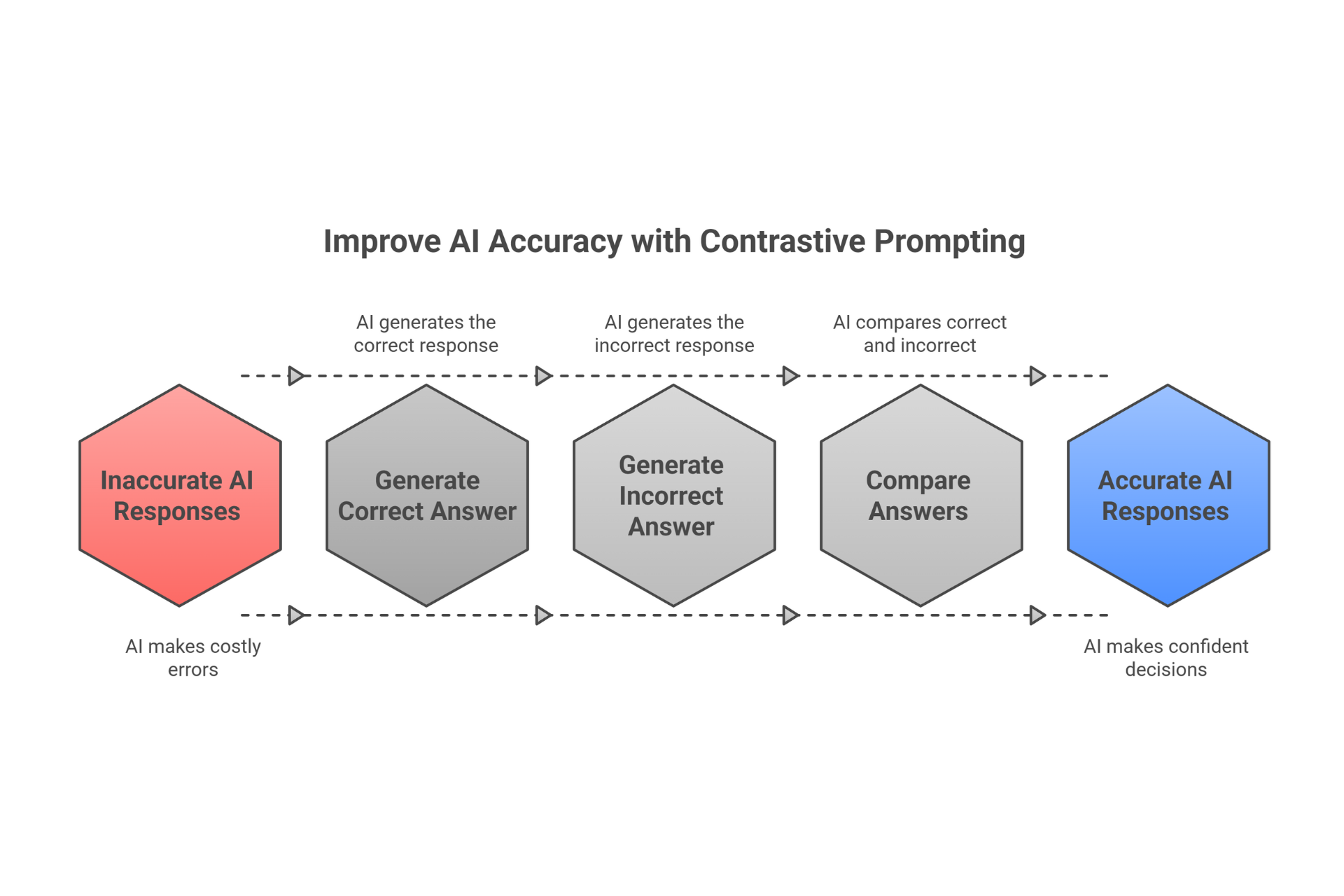
Method Card: Chain-of-Verification (CoV)
What it is:
AI generates an answer, then creates verification questions to check and correct itself. Like having a quality controller review work before submission. The AI becomes its own fact-checker and editor.
When to use:
- Creating legal documents or terms
- Writing technical specifications
- Producing client deliverables
- Any high-stakes content
Why it helps:
- Dramatically reduces errors and "hallucinations"
- Builds confidence in AI output
- Creates audit trail for decisions
SMB example prompt:
Answer, verify, then correct:
TASK: Update fitness studio terms & conditions
STEP 1: Draft updated T&Cs covering:
- Membership freezing policy
- Injury liability
- Payment terms
- Cancellation rules
- Equipment damage
STEP 2: Generate 5 verification questions:
- Are all scenarios covered?
- Any contradictions between sections?
- Irish/EU legal compliance issues?
- Clarity for average customer?
- Missing standard clauses?
STEP 3: Check each question against the draft
STEP 4: Provide the corrected final version
Context: Dublin fitness studio, 200 members, Sandyford location
Method Card: Causalised CoT (CauCoT)
What it is:
AI explicitly tracks cause-and-effect relationships between each reasoning step. Like a detective building a case, showing how each clue leads to the next. Every connection is explained with "because" and "therefore".
When to use:
- Diagnosing business problems
- Understanding market changes
- Analysing customer behaviour
- Troubleshooting operational issues
Why it helps:
- Makes hidden assumptions visible
- Prevents logical jumps
- Builds stronger arguments
SMB example prompt:
Track cause and effect through the problem:
Café sales dip analysis:
- Fact 1: Sales down 20% in last 6 weeks
- Fact 2: New competitor opened nearby 8 weeks ago
- Fact 3: Our prices unchanged for 2 years
- Fact 4: Customer complaints up about wait times
- Fact 5: Lost two experienced baristas 5 weeks ago
For each step, state:
CAUSE → MECHANISM → EFFECT
Step 1: Staff loss CAUSES longer prep time BECAUSE fewer skilled hands
Step 2: Longer prep CAUSES customer frustration BECAUSE office workers have limited lunch time
Step 3: [Continue chain...]
Root cause conclusion: [Based on causal chain]
Action plan: [Address root cause]
Method Card: Program-of-Thought (PoT)
What it is:
AI separates reasoning from calculation by writing simple code. Like using a spreadsheet formula instead of mental maths. The reasoning is in plain English, but calculations are precise code snippets.
When to use:
- Financial projections and modelling
- Inventory calculations
- Pricing strategies
- Data-heavy decisions
Why it helps:
- Eliminates calculation errors
- Handles complex maths accurately
- Creates reusable formulas
SMB example prompt:
Reason in words, calculate in code:
Boutique Q4 revenue projection:
REASONING:
"Last week we sold 280kg of beans across 3 shops. Sales usually grow 5% week-on-week in autumn, but rain in the forecast is likely to cut foot traffic by 8%. We're launching a loyalty campaign expected to lift sales 12%. Each kg makes ~50 cups, and we keep a 10% buffer stock. Beans cost €12/kg. I want to know how much to order and the cash needed."
CODE (illustrative Python - do not copy it):
# Last week's sales
last_week_kg = 280
# Factors
growth = 1.05
weather = 0.92
loyalty = 1.12
buffer = 1.10
price_per_kg = 12
# Projected demand
projected_sales_kg = last_week_kg * growth * weather * loyalty
# With buffer
order_qty_kg = projected_sales_kg * buffer
# Cost
order_cost = order_qty_kg * price_per_kg
print(f"Order: {order_qty_kg:.0f} kg of beans")
print(f"Cash required: €{order_cost:,.0f}")
INTERPRETATION: [Explain what the projection means for stock/staff planning]
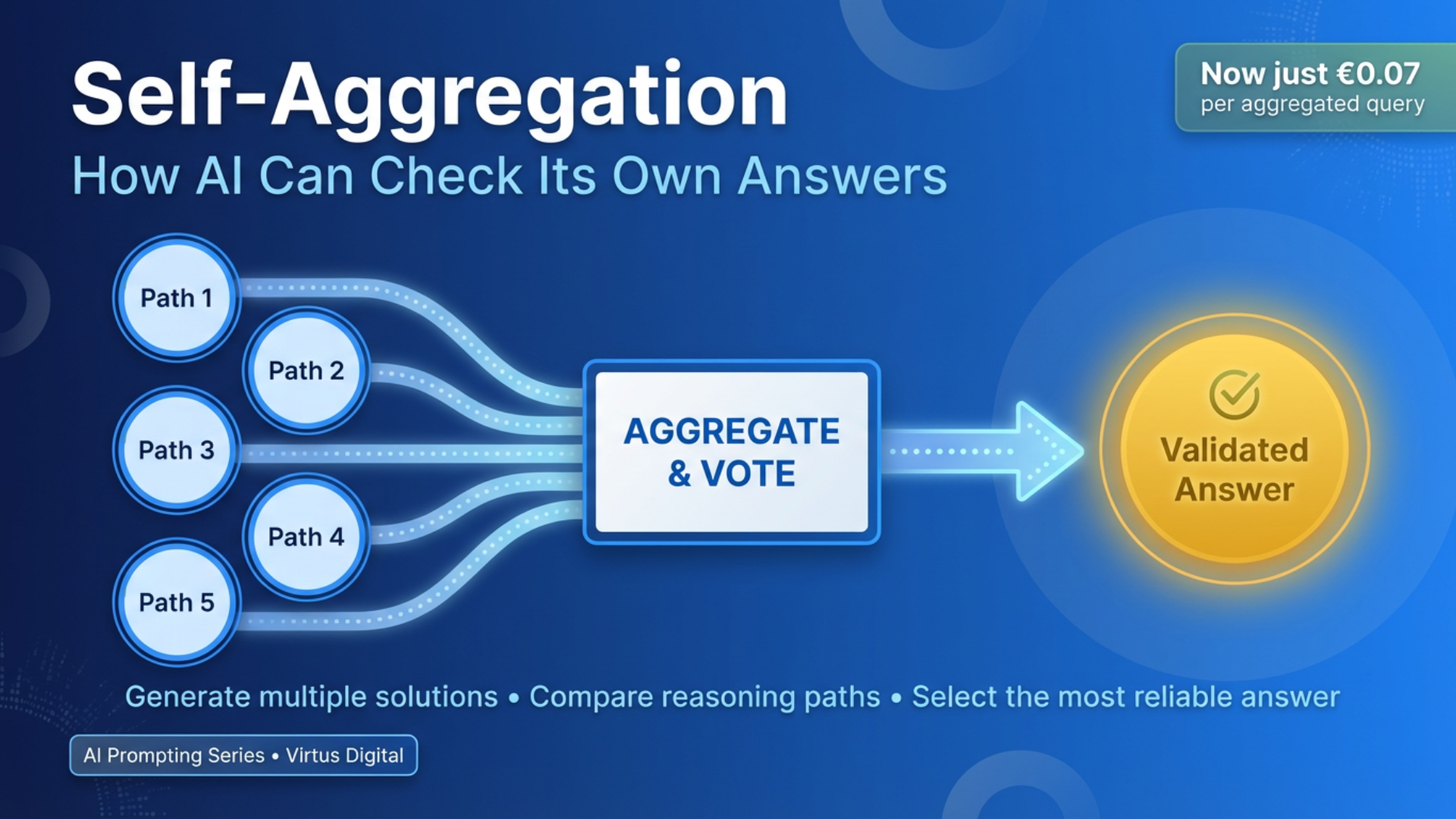
Method Card: Self-Organised CoT (SOCOT)
What it is:
AI determines its own best reasoning structure for your specific problem. Unlike basic CoT (you tell it to think step-by-step) or Strategic CoT (you tell it to plan first), SOCOT lets AI analyse your problem and choose its own methodology. Like hiring an expert consultant who selects their own framework based on the challenge.
When to use:
- Complex, multi-faceted challenges
- When unsure which method fits
- Analysing interconnected issues
- Strategic planning with many variables
Why it helps:
- Adapts to problem complexity automatically
- Combines multiple reasoning styles
- Handles ambiguous situations better
SMB example prompt:
Organise your own approach to solve:
B2B SaaS onboarding drop-off analysis:
- Current completion: 35% in first week
- Drop-off points: Email verify (10%), profile setup (25%), first project (30%)
- User feedback: "overwhelming", "too many features", "not sure where to start"
- Business impact: €15K monthly recurring revenue lost
- Resources: 1 developer, 1 designer, 2 weeks
Let AI choose:
1. What type of reasoning fits? (causal, comparative, systematic?)
2. What structure to use? (linear, tree, iterative?)
3. What aspects to prioritise? (UX, technical, psychological?)
Then solve using chosen approach: [AI organises solution method] [Applies method to solve problem] [Delivers structured recommendations]
Method Card: Chain-of-Reasoning (CoR)
What it is:
AI uses three reasoning modes in harmony: natural language (explaining simply), algorithmic (step-by-step process), and symbolic (formulas and calculations). Like having three experts collaborate on your problem.
When to use:
- Complex calculations with business context
- Technical problems needing clear explanation
- Multi-step processes with various components
- Teaching or training scenarios
Why it helps:
- Significantly outperforms single-mode reasoning (41% better in mathematical tasks)
- Catches errors through cross-validation
- Provides multiple perspectives
SMB example prompt:
Use three reasoning types together:
Pricing optimisation challenge: Current price: €50, Sales: 100/month, Costs: €30/unit
Natural Reasoning: "If we increase price, we'll lose some customers but make more per sale..."
Algorithmic steps:
- Calculate current profit
- Model demand elasticity
- Find optimal price point
- Validate against market
Symbolic/Formula: Profit = (Price - Cost) × Quantity If demand drops 2% per €1 increase... Optimal = derivative of profit function...
Synthesis: [Combine all three perspectives for final recommendation]
Method Card: Concept-Guided CoT (CGCoT)
What it is:
AI analyses through a series of guided conceptual questions, building understanding layer by layer. Like a consultant using a framework to assess your business systematically.
When to use:
- Comparing service offerings
- Evaluating marketing messages
- Assessing competitive positioning
- Reviewing content quality
Why it helps:
- Ensures comprehensive analysis
- Maintains consistent evaluation criteria
- Easier than rating on abstract scales
SMB example prompt:
Analyse through conceptual layers:
Compare two website homepages for conversion:
Concept: Trust signals
- Site A: What trust elements present?
- Site B: What trust elements present?
- Comparison: Which builds trust faster?
Concept: Value proposition
- Site A: How clearly communicated?
- Site B: How clearly communicated?
- Comparison: Which resonates better?
Concept: Call-to-action
- Site A: Visibility and clarity?
- Site B: Visibility and clarity?
- Comparison: Which drives action better?
Overall: [Synthesise which converts better and why]
Method Card: Constrained CoT (CCoT)
What it is:
Standard chain-of-thought reasoning but with strict length limits. Forces AI to be concise whilst maintaining accuracy.
When to use:
- Quick email responses
- Social media content planning
- Brief reports or summaries
Why it helps:
- Reduces costs significantly
- Prevents rambling responses
- Maintains focus on essentials
SMB example prompt:
Solve step-by-step in under 100 words:
Calculate ROI for email campaign: Cost €500, sent to 5,000, open rate 20%, click rate 5%, conversion 2%, average order €75.
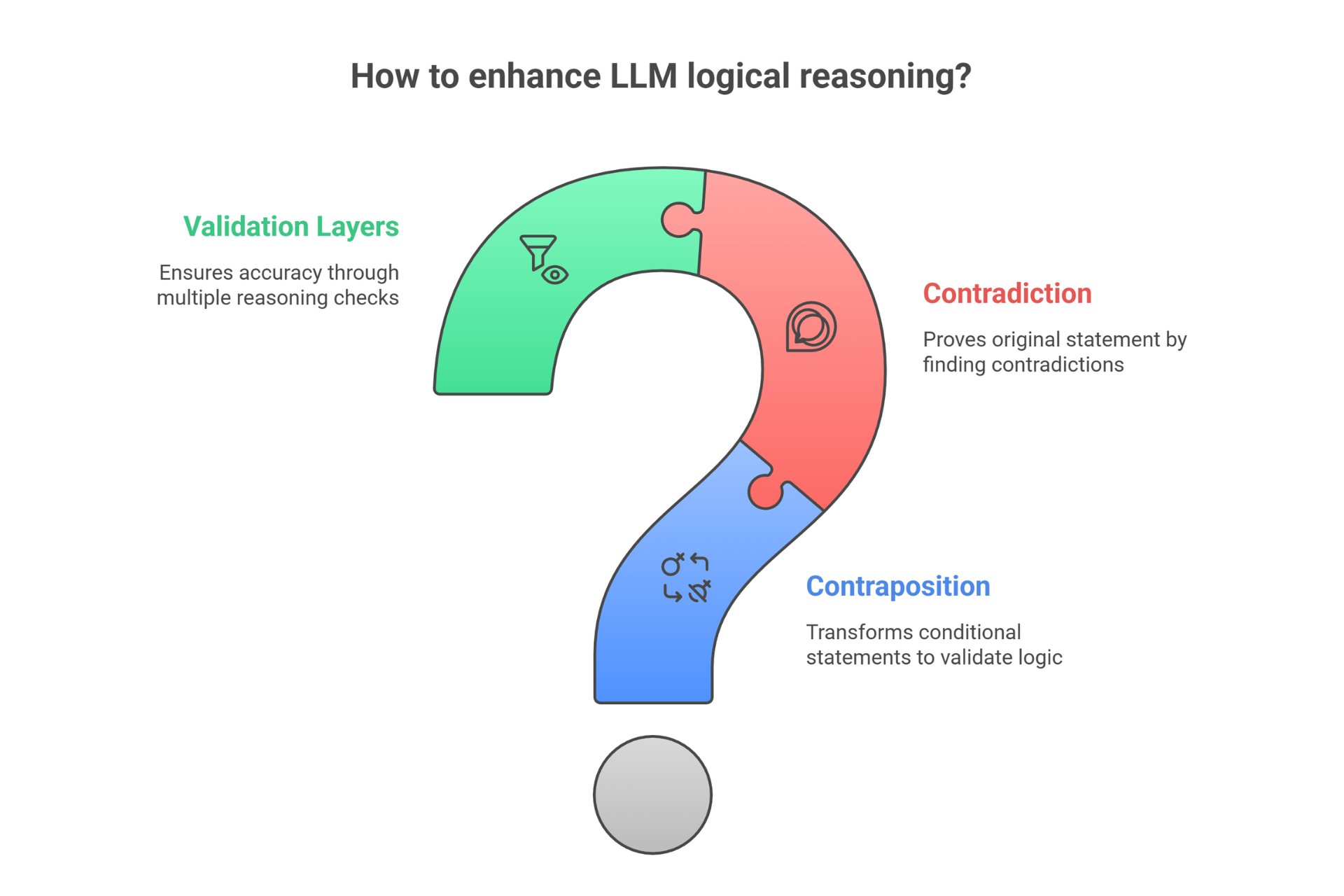
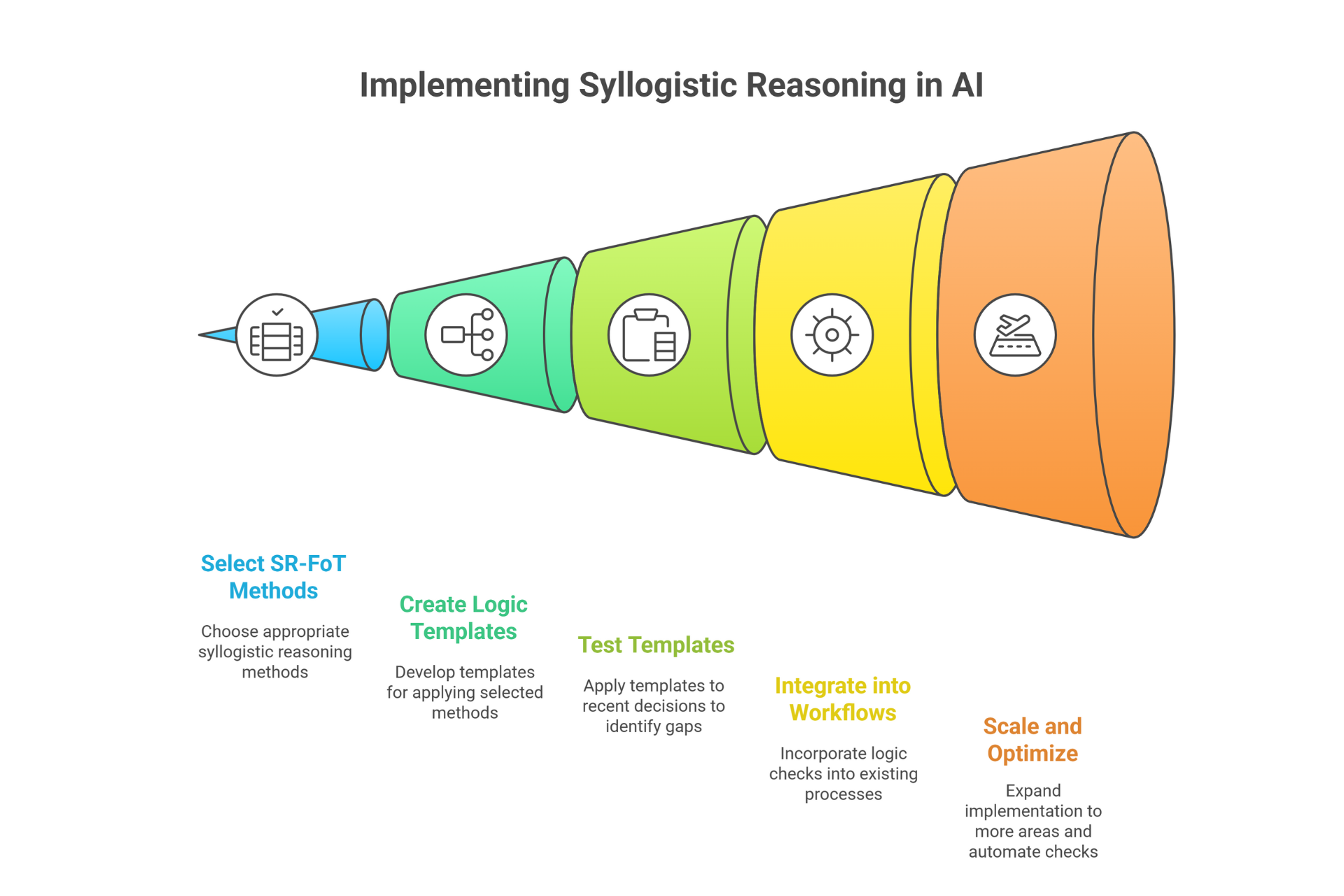
Method Card: Syllogistic Reasoning (SR-FoT)
What it is:
AI uses formal logical reasoning, building from premises to conclusions. Like a lawyer building a case with clear logical steps.
When to use:
- Policy decisions
- Eligibility assessments
- Compliance checking
Why it helps:
- Rock-solid logical foundation
- Eliminates reasoning errors
- Clear documentation trail
SMB example prompt:
Use logical premises to conclude:
Premise 1:
All premium members get free delivery
Premise 2:
Orders over €50 qualify for premium trial
Premise 3:
Customer ordered €65
Question: Does customer get free delivery? Show logical steps.
Copy-and-paste prompt templates
Local café: weekday footfall promotion (CoG)
Improve then answer my marketing question:
Original: "How do I get more weekday customers?"
Constraints:
- Budget: €500/month max
- Location: Near IFSC/Docklands offices
- Problem: 25% weekday drop
- Timeline: Need results in 4 weeks
Step 1: Rephrase to be more specific
Step 2: Identify what details matter most
Step 3: Create best version of question
Step 4: Answer with 3 specific, costed tactics
Dental clinic: treatment page rewrite from messy notes (ISP2)
Process my rough notes into a patient-friendly treatment page:
Raw notes: "Dental implants info - expensive but worth it, €2000-3000 per tooth, takes 3-6 months total, need good bone density might need graft, success rate 95%, looks natural, careful with smoking affects healing, payment plans available 0% 12 months, consultation €95 includes scan"
Instructions:
- Extract all key facts
- Rate reliability (1-5) of each claim
- Identify missing crucial info
- Organise into logical sections
- Write page with headers, benefits, process, costs
Audience: Anxious patients comparing options in Dublin Tone: Professional yet reassuring
Fashion e-commerce: Product page conversion mini-audit (SCoT)
Strategic quick audit of product pages:
Plan First:
- Identify audit framework
- List checkpoints
- Prioritise by impact
Then Audit:
- URL: [fashion-site.com/summer-dresses]
- Current conversion: 1.2%
- Bounce rate: 65%
- Add-to-cart: 3.5%
- Cart abandonment: 70%
Constraints:
- Budget: €2,000
- Timeline: 2 weeks
- Tech limits: Shopify Plus
Output: 5 quick wins ranked by ROI
Marketing agency: monthly PPC summary under token budget (CoD)
Ultra-concise PPC performance summary:
Draft Steps (5 words each):
- Spend versus budget status
- Cost per click trend
- Conversion rate this month
- Best performing ad group
- Worst performing keywords identified
- Recommended bid adjustments needed
Data: Budget: €5,000, Spent: €4,750 Clicks: 1,900, Conversions: 38 Last month conversions: 42
Final Output: Professional client summary paragraph (100 words max)
Plumbing services: winter boiler offer selection (ToT)
Explore all options, pick best:
Context:
- January typically 30% quieter
- €1,000 promotion budget
- Need bookings, not just enquiries
- Competitors offer free annual service
Explore Paths: Path A: 20% off all boiler repairs Path B: Free boiler health check (valued €65) Path C: Book 2 services, get 3rd free
For each path:
- Customer appeal (1-10)
- Profit impact
- Operational feasibility
- Competitive advantage
Decision: Choose with clear reasoning
Fitness studio: T&Cs refresh with self-check (CoV)
Draft, verify, then perfect our terms:
DRAFT new membership terms covering:
- Freezing: Max 3 months/year, €10/month
- Cancellation: 30 days notice
- Classes: Book max 3 advance
- Injuries: Member responsibility
- Payments: Direct debit only, failed = €15 fee
VERIFY by asking:
- Any contradictions?
- All scenarios covered?
- Legally compliant?
- Fair to both parties?
- Clear to average person?
CHECK each point
CORRECT issues found
Output: Final polished version
Café sales dip diagnosis with cause → effect chain (CauCoT)
Build causal chain for problem:
Facts:
- Week 1: Sales normal
- Week 2: Hired new staff
- Week 3: Negative review posted
- Week 4: Sales down 15%
- Week 5: More complaints logged
- Week 6: Sales down 20%
Build Chain: Event → Because → Therefore → Leading to
Example: New staff hired → Because experienced barista left → Therefore service slower → Leading to customer frustration → Therefore negative review → Leading to...
Conclusion: Root cause and fix
Boutique retailer: simple Q4 revenue projection (PoT)
Project Q4 revenue using clear logic:
Reasoning (plain English): "Last year Q4: €45,000. Adding premium range should boost 20%. But cost-of-living means fewer big purchases, estimate -10% impact. Black Friday is 35% of Q4."
Calculation (show as code): base_q4 = 45000 premium_boost = 1.20 economy_impact = 0.90 projection = base_q4 * premium_boost * economy_impact
Result: €48,600
What This Means: Stock ordering deadline? Staff needs for peak? Marketing budget allocation?
B2B SaaS: onboarding drop-off analysis (SOCOT)
You decide how to analyse this:
Problem: Only 35% complete onboarding week 1
Drop-Off Data:
· Email verify: 10% lost
· Profile setup: 25% lost
· First project: 30% lost
· Team invite: 5% lost
Feedback Themes: "Too complex", "Overwhelming", "Not sure why I need this", "Where's the value?"
Your Task:
- Choose analysis method (causal? comparative? systematic?)
- Apply chosen method
- Identify top 3 fixes
- Prioritise by effort/impact
Resources: 1 dev, 1 designer, 2 weeks
Practical checklist: how to brief AI effectively
Start with the method name - Tell AI explicitly which Chain-of-X method to use (e.g., "Use Tree of Thoughts to explore options")
Set clear constraints - Always include budget, timeline, resources, and any limitations upfront
Provide complete context - Include actual numbers, not vague descriptions ("sales down 20%" not "sales dropped")
Request specific outputs - Ask for "3 tactics costing under €200 each" not "some ideas"
Include validation steps - Add "check your reasoning" or "verify assumptions" to catch errors
Specify format needed - Tell AI if you need bullets, paragraphs, or structured sections
Use plain language - Avoid jargon in your prompts; write as you'd explain to a colleague
Give examples when possible - Show AI your preferred style with a brief sample
Do I need special tools to use these methods?
No, these methods work with any AI chat interface (ChatGPT, Claude, etc.). Simply copy the templates and adapt them to your needs. No coding or technical knowledge required.
Will this reduce my AI costs?
Yes, especially methods like Chain of Draft (CoD) which use dramatically fewer words. Even basic CoT prevents costly back-and-forth clarification, substantially reducing overall usage.
What order should I use these methods in?
Start with basic Chain of Thought for general problems. Add Chain-of-Guidance when your question needs refining. Use specialised methods (ToT, CoV, CauCoT) for specific challenges. Combine methods as you get comfortable.
Appendix: Resources Used
Research Papers & Studies Referenced
The methods in this guide are based on the following academic research:
Core Chain-of-Thought Research:
- Wei et al. - "Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models"
- "Beyond Chain-of-Thought: A Survey of Chain-of-X Paradigms for LLMs"
Specific Method Research:
- ISP2: "Understanding Before Reasoning: Enhancing Chain-of-Thought with Iterative Summarization Pre-Prompting"
- Tree of Thoughts (ToT): "Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models"
- CauCoT: "Unveiling and Causalizing CoT: A Causal Perspective"
- CGCoT: "Concept-Guided Chain-of-Thought Prompting for Pairwise Comparison Scoring of Texts with Large Language Models"
- Chain-of-Reasoning (CoR): "Chain-of-Reasoning: A Unified Mathematical Reasoning Approach Through Multi-Paradigm Perspective" (arxiv.org/pdf/2501.11110)
- SR-FoT: "Syllogistic Reasoning Framework of Thought"
- ECHO: "Self-Harmonized Chain of Thought"
- Chain of Draft (CoD): Research on minimalist reasoning approaches
- Program of Thought (PoT): Studies on separating reasoning from computation in LLMs
- Chain-of-Verification (CoV): Research on self-verification mechanisms in language models
Additional Studies:
- Research on constrained reasoning (CCoT)
- Studies on self-organised reasoning patterns (SOCOT)
- Strategic planning in AI reasoning (SCoT)
- Chain-of-Guidance methodology research
Note: All methods presented have been adapted for practical SMB use without requiring technical implementation or access to the original research papers.
Next steps in your AI prompting journey
Master these Chain-of-X methods and transform how AI works for your business. Get the complete toolkit with templates, video tutorials, and industry-specific examples.
Explore the full AI Prompting Series, templates and updates:
https://virtusdigital.ie/ai-prompting-series